Table of Contents
Powers of High Court. ??
High Courts are the 2nd Important Judiciary stage of India and the highest in State. It operates below the Supreme Court but enjoys many powers, so today we will overview the powers of high court.This is the main topic respective to Indian Polity for UPSC Exam and other state services.
In the British India period, high courts were originated by Lord Canning in 1862. Calcutta, Madras, and Bombay were the 1st three cities where High Courts were started. Later on, in the year 1866 4th high Court was started in Allahabad.
According to our Constitution high court must be for every state separately. After the 7th Amendment Act of 1956, Parliament got the power to make common high courts to 2 – 3 states or Union territories.
At present there are about 25 total High Courts in India. There are a total of 1079 Judges where 771 are permanent, and the remaining 308 are additional Judges.
Delhi is the only union territory which has had its own high Court since 1966.
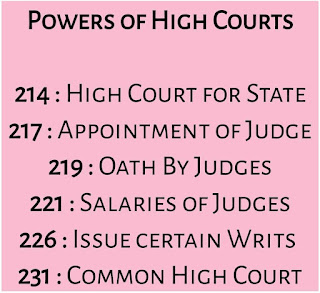
Articles from 214 to 231 belong to the powers and functions of the high court. While it belongs to Part VI of the Indian Constitution.
Let’s see the basic functions of High Court. ✌✌
Organization of Indian High Court:-
President plays a key role in selecting no. Judges in the High Court. As per the Constitution, there is no fixed strength for no Judges given but President has to appoint Judges as per workload. Also strictly there should be 1 Chief Justice and the rest other Judges for Indian high courts.
Judges of Indian High Court:-
The appointment is done by the President of India, discussing it with Chief Minister and Governor. In the case of the common high court, President discusses with all governors of States and Union territories.
How to become a High Court Judge in India:- ??
1) He should be an advocate of the High Court for 10 years.
2) He must have worked with Judicial Office for 10 Years.
3) He must be a citizen of India.
4) There is no minimum age for the appointment of High Court Judges.
Oath of Judge:-
1) He must follow the Indian Constitution
2) He will uphold the Sovereignty and Integrity of India i.e Preamble of Indian Constitution
3) He will follow his job without any fear and not in any bodies’ favor.
 |
| Power-High-court |
Tenures of Judges of Indian High Court:-
1) There is no fixed term, but he holds office till the age of 62.
2) He can be removed by President on the recommendation of Parliament
3) He leaves his office on promotion for Supreme Court or any other high court
4) He must resign to President by writing a letter
Removal of Judges:- ??
He can be removed by the President of India on the recommendation of the Parliament of India. Parliament must pass the removal order with a 2/3 special majority. He can be removed by only incapacity or misbehavior. He is removed in the same manner as Supreme Court Judge.
In the Judges Enquiry Act (1968) there were many conditions given for the Removal of Judges, they are:-
1) Removal Motion must be signed by 100 members in Loksabha or 50 members in Rajya Sabha and gives to Speaker.
2) Speaker may accept or refuse it
3) 3 Member body is made to investigate the whole process
4) If the committee finds him guilty then the Houses of Parliament pass a resolution and sends it to the President.
Salaries and Allowances of Judges:-
It depends from time to time in Parliament. In 2009 changes were made and the salary was increased for Chief Justice as well as other Judges. Retired Judge gets a monthly pension of 50 %.
Transfer of Judges:-
He can be transferred by discussing it with the Chief Justice of India. He can be transferred from one high court to another high court, which is common for 2 states. Transfer Judge can demand Judicial Review to Supreme Court.
Acting Chief Justice of Indian High Court:-
President can appoint acting Chief Justice
1) When the Office of Chief Justice of High Court is Vacant
2) Chief Justice of the High court is absent
3) If he is not behaving properly as per Rules and Regulations
Retired Judges:-
At any time Chief Justice of the High Court has the right to appoint a retired Judge in his pannel. But he has to take the permission of the President and the person he is appointing. An appointed person enjoys all rights that other Judges have.
Other Independent Rights of High Court:-
1) Freedom to appoint their Staff
2) If transfer by senior they are challenged it
3) Take as much as time to give results of any court
4) Parliament and President cannot interfere in their Work
5) After retirement, they can’t work
Some of the important and old high courts in India are the Bombay High Court, Calcutta High Court, and Madras High Court.
Important powers of High Court:-
There are many important other provision and powers of the high court which save our Fundamental Rights while living in India.
They are
1) A court of record
2) Appellate Jurisdiction:-
This includes Civil Matters and Criminal Matters.
3) Writ Jurisdiction:-
It means any citizen who thought that his fundamental rights are violated, he can directly move to the High courts of India for justice.
4) Original Jurisdiction:-
This is the most interesting powers of the High court of India which says that some of the cases will be heard in its proposal or instance. This includes cases like marriage, Divorce, Election disputes, the act of revenue collection, Fundamental rights of citizens.
5) Supervisory Jurisdiction:-
It is the power of superintendence over all other courts.
6) Control over Subordinate Courts:-
High courts had good control and supremacy on subordinate courts. It can withdraw case which is pending in subordinate courts.
7) Power over Judicial Review
Name – Year – Seats of High Courts:-
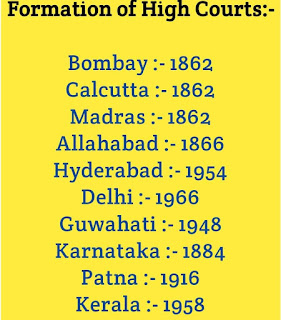
1) Bombay – 1862 – Mumbai
2) Calcutta – 1862 – Kolkata
3) Madras – 1862 – Chennai
4) Allahabad – 1866 – Allahabad
5) Hyderabad – 1954 – Hyderabad
6) Chattisgarh – 2000 – Bilaspur
7) Delhi – 1966 – Delhi
8) Guwahati – 1948 – Guwahati
9) Gujarat – 1960 – Ahmedabad
10) Himachal Pradesh – 1971 – Shimla
11) Jammu and Kashmir – 1928 – Srinagar and Jammu
12) Karnataka – 1884 – Bengaluru
13) Kerala – 1958 – Ernakulam
14) Madhya Pradesh – 1956 – Jabalpur
15) Jharkhand – 2000 – Ranchi
16) Manipur – 2013 – Imphal
17) Meghalaya – 2013 – Shillong
18) Orissa – 1948 – Cuttack
19) Patna – 1916 – Patna
20) Punjab and Haryana – 1875 – Chandigarh
21) Rajasthan – 1949 – Jodhpur
22) Sikkim – 1975 – Gangtok
23) Tripura – 2013 – Agartala
24) Uttarakhand – 2000 – Nainital
 |
| powers-high-court |
Important articles of High Courts in India:-
1) 214:- High Courts of States
2) 216:- Constitution of High Courts
3) 217:- Appointment of Judge of High Court?
4) 219:- Oath by Judges of Indian High Court
5) 221:- Salaries and other allowances of Judges
6) 222:- Transfer of Judge from one High Court to another High Court
7) 223:- Appointment of acting Chief Justice
8) 225:- Jurisdiction of existing High Courts
9) 226:- Power of high courts to issue certain Writs
10) 228:- Transfer of certain cases to High Court
11) 230:- Extension of Jurisdiction of High Courts to Union territories
12) 231:- Establishment of common High Court for two or more States.
Conclusion:-
In this article, you learned how powerful high courts are there. They are a totally Independent body and enjoy all their powers.
Here we discussed the Salaries of Judges, How they are appointed, Term of Judges, the Impeachment Process, Powers of High Courts, and then Functions of High Court.
The important list of High Courts, their establishment years, and their bench is given there. This is the most important topic for Indian polity from the UPSC exam point of view. Hope all of you students would have understood the topic powers of high court.
JAY HIND….!!!!
