Table of Contents
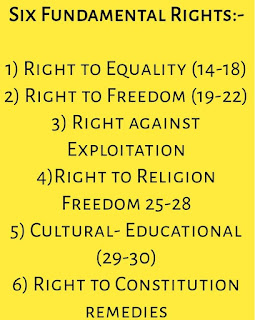
Fundamental Rights in India / Six categories of Fundamental Rights
The Fundamental Rights are included in Part 3 of the Constitution from Articles 12 to 35.
What are the 6 important fundamental rights in India?
1) Right to equality (Article 14-18)
The right to equality means equality for all before the law. No one will have discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, gender, or place of birth.
Equality of opportunity in matters of employment, the abolition of untouchability, and the abolition of titles.
2) Right to freedom (Article 19-22)
The right to freedom explains freedom of speech and expression to every citizen also assembly.
Association or union or cooperatives, movement, residence, and right to practice any profession or occupation.
3) Right against exploitation (Article 23-24)
The right against exploitation prohibits all forms of forced labor, child labor, and trafficking of human beings.
4) Right to Freedom of Religion (Article 25-28)
The right to freedom of religion says freedom of worshipping and free profession, practice, and following of religion.
Also, freedom to manage religious affairs, freedom from certain taxes, and freedom from religious instructions in certain educational institutes.
5) Cultural and educational rights (Article 29-30)
The Cultural and Educational Rights give the right to any section of citizens to conserve their culture, language, or script.
And the right of minorities to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.
6) Right to Property (Article 31)
7) Right to Constitution remedies (Article 32)
But in the Emergency period, however, the Right to property was deleted from the list of Fundamental Rights by the 44th Amendment act, 1978.
They are not permanent in Constitution, they can be changed or canceled.
Importance of Fundamental rights:-
Fundamental Rights of India are only available to Indians, not foreigners are below:-
1) Public Employment (article 16)
2) Protection of Language, script, and culture of minorities (article 29)
3) Right of minorities to est college(article 30)
Many good things had been included such as the abolition of Untouchability and Titles were done.
- The right to education was included under the 86th amendment act of 2002.
Following are all Fundamental Rights below:-
Article 12:- Definition of state
Article 13:-Derogation of Fundamental Rights
Article 14:-Equality before the law
Article 15:-Prohibition of Discrimination under religion, caste, sex
Article 16:-Equality of opp in matters of Public Unemployment
Article 17:-Abolition of Untouchability
Article 18:-Abolition to Titles
Article 19:-Protection regarding freedom of Speech
Article 20:-Protection in respect of convention for offenses
Article 21:-Protection of Life and personal liberty
Article 21A:-Right to education
Article 22:-Protection against arrest and law.
Article 23:-Prohibition of Traffic in Human beings and forced labor
Article 24:-Prohibition of Employment of children in factories
Article 25:-Freedom of conscience
Article 26:-Freedom to manage religious affairs
Article 27:-Freedom for payment of taxes for promotion of religion
Article 28:-Religious worship in certain educational institutions
Article 29:-protection of Interests of minorities
Article 30:-Right to the minority for educational institutions
Article 31:-Compulsory acquisition of property (removed)
Article 32:- Constitutional Remedies. The heart of Cont.
Article 33:-Power of Parliament to modify the rights conferred by this part
article 34:-Restriction on rights conferred by this Part while martial law is in force in any area
Article 35:-Legislation to give effect to the provisions of this part.
If we violate fundamental rights then we can be punished by the Indian Judiciary. But in the case of Fundamental duties case is not the same.
Who can suspend the fundamental rights in India?
Who is the protector of fundamental rights in India?
Which fundamental right is abolished by Constitution?
Who can claim Fundamental Rights?
Who is the Father of fundamental rights in India?
JAY HIND….!!!!